Acoustic Anomaly Detection 🎵
Project Details
This research investigates the application of unsupervised learning techniques to detect anomalies in acoustic signals within the automotive industry. The goal is to automate the identification of customer-relevant noise issues by analyzing audio recordings from vehicle components. The system employs feature engineering and deep learning models to cluster normal and abnormal sound patterns, reducing the need for manual annotation.
The hypothesis states that an unsupervised model can distinguish between normal and anomalous sounds by extracting relevant audio features and clustering similar patterns. The system processes signals recorded during window movements in vehicle doors, identifying deviations from expected acoustic behavior. (see source code)
Key Features
- Unsupervised Anomaly Detection: Implements clustering techniques to identify outlier sounds without prior labeling.
- Feature Engineering & Deep Learning: Uses statistical descriptors and autoencoders to extract meaningful representations of acoustic signals.
- Real-World Automotive Application: Tested on vehicle window movement sounds to detect mechanical issues automatically.
My Contribution
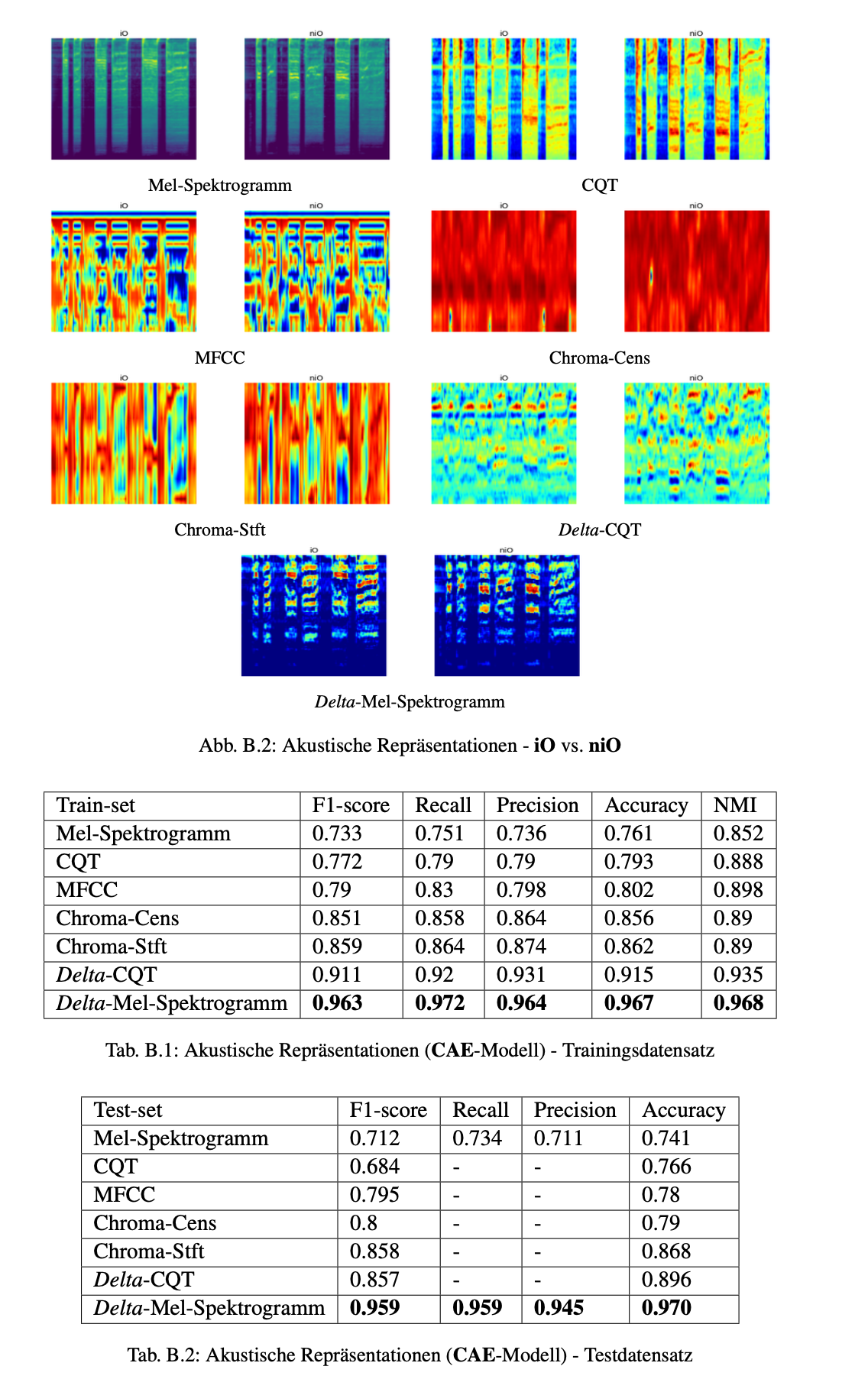
I developed and optimized the system by implementing feature engineering techniques to manually extract signal descriptors and designing a deep clustering model using convolutional autoencoders to automatically detect anomalies. I evaluated the effectiveness of both traditional clustering methods, such as k-Means, and deep learning approaches. Additionally, I improved data preprocessing by applying noise reduction techniques, standardizing input features, and optimizing the transformation of raw audio signals into Mel-Spectrogram representations. I also refined evaluation metrics to ensure reliable performance assessment, contributing to the overall robustness and scalability of the system.
Challenges and Solutions
- High-Dimensional Data: Reduced computational complexity by transforming raw audio signals into compact Mel-Spectrogram representations.
- Noise & Variability: Standardized data collection procedures and applied augmentation techniques to improve model robustness.
- Evaluation Without Labels: Employed unsupervised clustering validation techniques and visualized latent feature spaces using t-SNE.
Outcome
- Successfully demonstrated that deep clustering methods outperform classical feature-engineering-based approaches.
- Developed a framework capable of detecting multiple types of anomalies in real-world automotive scenarios.
- Provided insights for improving vehicle quality control by identifying potential mechanical issues early.
- Used exclusively unsupervised methods, eliminating the need for labeled data and significantly reducing time and cost.
Technologies
Python TensorFlow Keras Unsupervised Learning Deep Clustering AutoEncoders Embeddings Acoustic Signals Mel-Spectrogram IDEC t-SNE Deep Clustering Feature Engineering